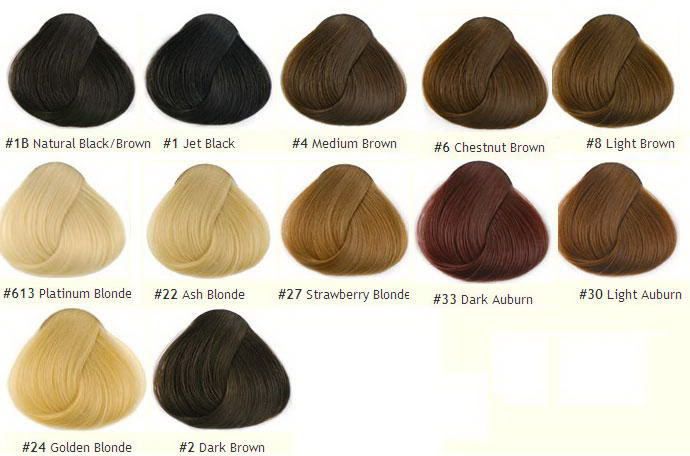
Human hair color is determined by the pigment melanin, which is found in the hair. It comes in two forms: eumelanin and pheomelanin. The more melanin there is, the darker the hair will be. If there is less melanin, the hair will be lighter.

Black
The pigmentation of Hair is very different between animal and human hair. Animals have more pigmentation and are blacker than humans. It’s not possible to get truly black hair from your natural Hair, though. You need to go through a chemical dyeing process or use henna. Hair dye is an artificial coloring that was created by scientists. It has several components, including resorcinol, ammonia, and ammonium chloride.
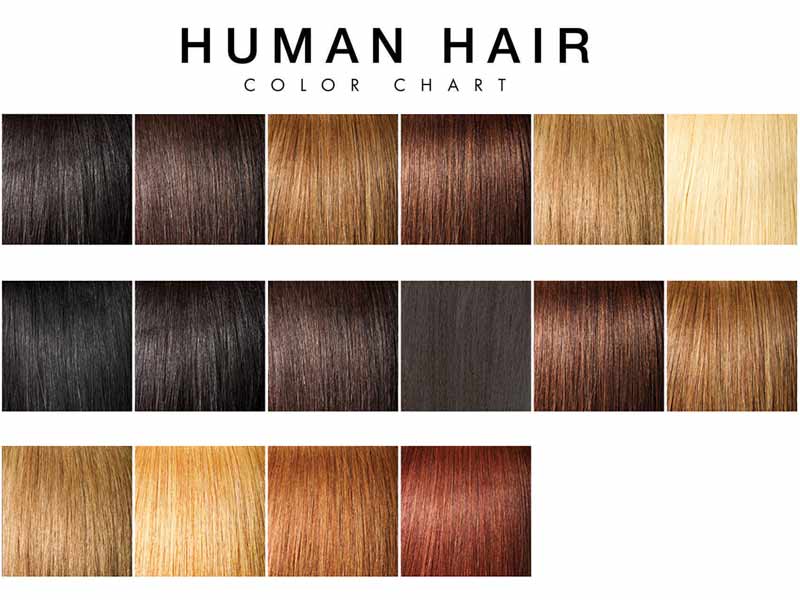



The type of melanin in your Hair is determined by many genes. The best-studied gene for human hair color is MC1R, which provides instructions for the production of melanocortin 1 receptor, a molecule that controls the type of melanin produced by the melanocytes. Several other genes also play a role in the regulation of melanocytes.

Brown
Human hair color consists of two types of pigments, eumelanin (dark) and pheomelanin (light, reddish). The more eumelanin, the darker the hair. Every strand of Hair is made up of both pigments, and every person has some eumelanin in their hair. Even light blonde or jet black hair contains some brown eumelanin.
While the word brunet is typically associated with women and girls, men and boys can also have brown hair. According to Merriam-Webster, a brunet is a person with brown hair. It is more common to say “he has brown hair” than “she’s a brunette.”
Although the genetics of human hair color isn’t well understood, researchers have found that at least two gene pairs are responsible for hair color. The dominant brown allele results in brown hair, and the recessive blonde allele results in blonde hair. A child with two brown-haired parents can have both brown and blonde hair. The not-red gene suppresses the production of pheomelanin, which is responsible for hair color.
Blonde
Blonde hair color is caused by the presence of certain genes. These genes affect the appearance of the eye and skin. They also play a role in the production of the pigment eumelanin. However, if these genes are turned off, the production of eumelanin is reduced. This is a genetic change that may lead to the appearance of blond hair.
Red
The red hair color is inherited through a complex series of genetic variations. The MC1R gene is responsible for the amount of red pigment in our hair. Other genes determine the amount of brown pigment. Although the MC1R gene is responsible for red hair, many other factors also play a role. Consequently, two red-haired parents can have children without red hair.
To find out why some people have red hair, researchers have identified genetic markers linked to the pigmentation. These SNPs are located in regions of the genome that are not important for protein synthesis. These SNPs may be responsible for red hair pigmentation, but the exact genetic mechanisms involved are not known.
Griscelli syndromes
Griscelli syndromes are a rare hereditary disorder characterized by distinctive hair and skin color. Patients may also have neurological or immune system problems. The syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. The mutated gene in Griscelli syndromes causes the disorder. Genetic testing is required to make the correct diagnosis. Some cases of Griscelli syndromes can be treated with stem cell transplantation.
Type 1 Griscelli syndrome is characterized by a deficiency in the MY05A gene, resulting in hypopigmented skin and hair. The affected individuals are more susceptible to infections and develop hemophagocytosis, an abnormality of the immune system that damages tissues and organs. Patients with this disorder often experience recurrent infections. Neurological defects are also common.
White in albinism
Albinism is a genetic condition that results in the loss of melanin, the pigment that gives skin and hair color. Albinism is often unnoticed, although it has been the subject of numerous popular myths and villains. People with albinism often look different from their racial peers and are often subject to misunderstandings and discrimination.
The most common form of albinism is oculocutaneous albinism. This is a result of a defect in a gene called tyrosinase. Tyrosinase is a key enzyme in the production of melanin. In individuals with OCA1A or OCA1B albinism, this enzyme is inactive or minimally active. Consequently, patients with albinism have white hair or blond hair.
In some cases, people with albinism also have reddish or yellow hair. However, their hair color may darken by early adulthood. As a result, they should wear sunscreen with an SPF of at least 20 to avoid sun damage. Moreover, people with albinism should report any change in their skin color or hair color. Their eyes may also have different shades of red or blue, but they are usually a light brown color.
MC1R gene
The MC1R gene plays a role in hair pigmentation. It has been linked to red hair. Several studies have found that red hair is associated with polymorphisms in the MC1R gene. These findings raise expectations for the future study of other human pigmentation traits.
The MC1R gene is found in both sexes and most people carry two copies from both parents. This gene is responsible for the color of our hair and produces a high level of eumelanin. About 90 percent of us have brown or black hair. People with red hair have a variant in the MC1R gene known as rs368507952 (R306H) and rs200000734 (R213W).
While there are many different MC1R variants, they all have some significant associations with red hair. In a study of Icelanders, a genetic variation in MC1R was associated with red hair. The authors noted that while this gene is the main determinant for red hair, other genetic factors must also be present in order to change the hair color.
ASIP gene
Human hair color is inherited through a genetic variation. The ASIP gene carries two different promoter haplotypes, VP and HCP. The two promoters regulate the activity of the ASIP gene in different body regions. The Ventral Promoter predominantly activates the ASIP gene on the ventral surface of the body, while the Hair Cycle Promoter controls the activity of the ASIP gene on the dorsal surface.
The ASIP gene also affects coat pigmentation in dogs. The ASIP gene has been associated with the red sesame coat color in dogs.
MC1R variants
Human hair color is largely inherited and influenced by genetic variation in the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R) gene. There are more than 80 known MC1R variants. Population-based studies indicate that between one and 2% of individuals carry at least one variant allele. Despite their low prevalence, these variants are thought to play a role in the development of a person’s hair color.
There are two types of MC1R variants. One is a coding variant that varies in minor allele frequency in different populations, while the other is a non-coding variant. Depending on the population, the MC1R variants may affect the appearance of hair colour in a different way.
SNPs in ASIP gene
The ASIP gene is associated with red, blond, and brown hair colors. It also affects skin pigmentation. Its associated SNPs are rs1540771 and rs62389424. These two SNPs are located approximately 34 kb apart and are known to affect the pigmentation of the skin and hair.
The study found associations between SNPs in the ASIP gene and hair colour in a Danish and Scottish population. Although the findings are still preliminary, they point to novel associations between these genes and human hair color. Similarly, associations between SNPs and eye colour were detected in Danish and Scottish populations.
Recent progress in DNA prediction of human eye color has raised expectations for predicting other pigmentation traits in humans. Moreover, red hair color is already explained to a large extent by SNPs in the MC1R gene. Valverde et al. (1995) showed that polymorphisms in this gene were associated with red hair color, and this was confirmed by numerous other studies in various population samples.

